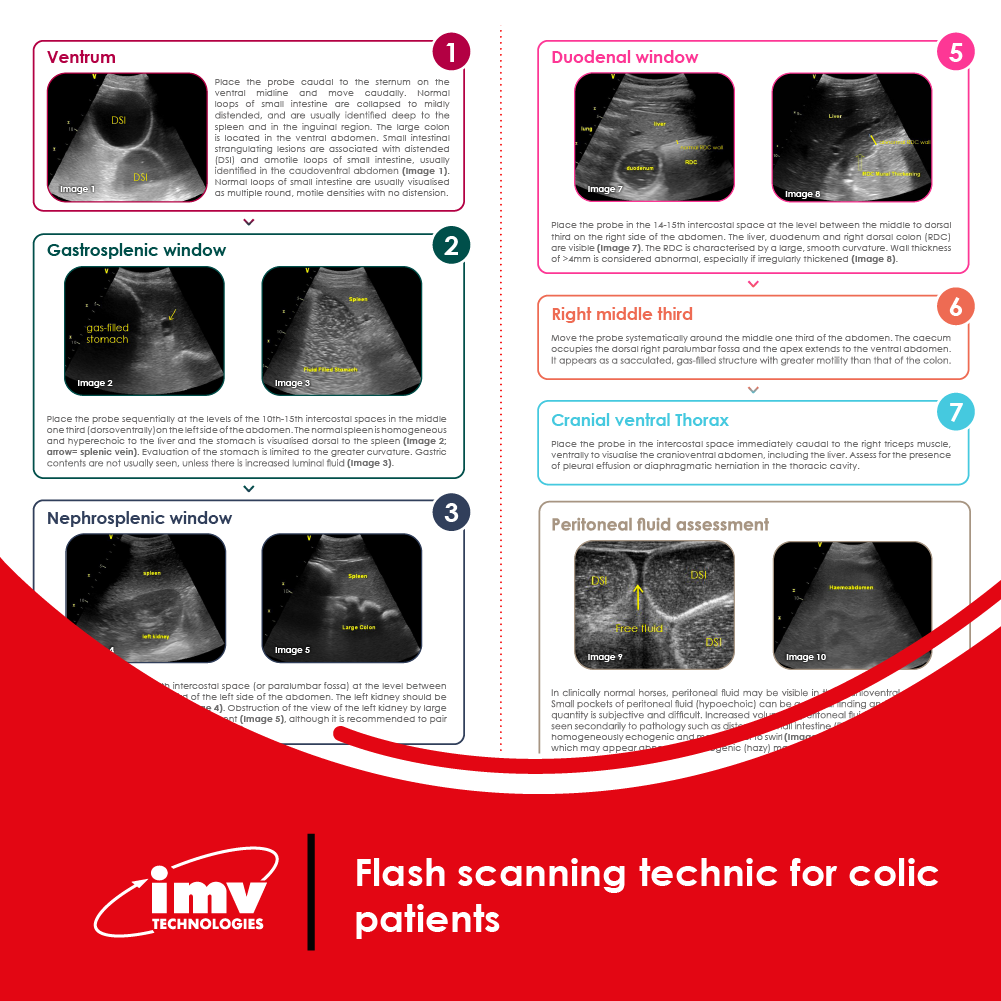
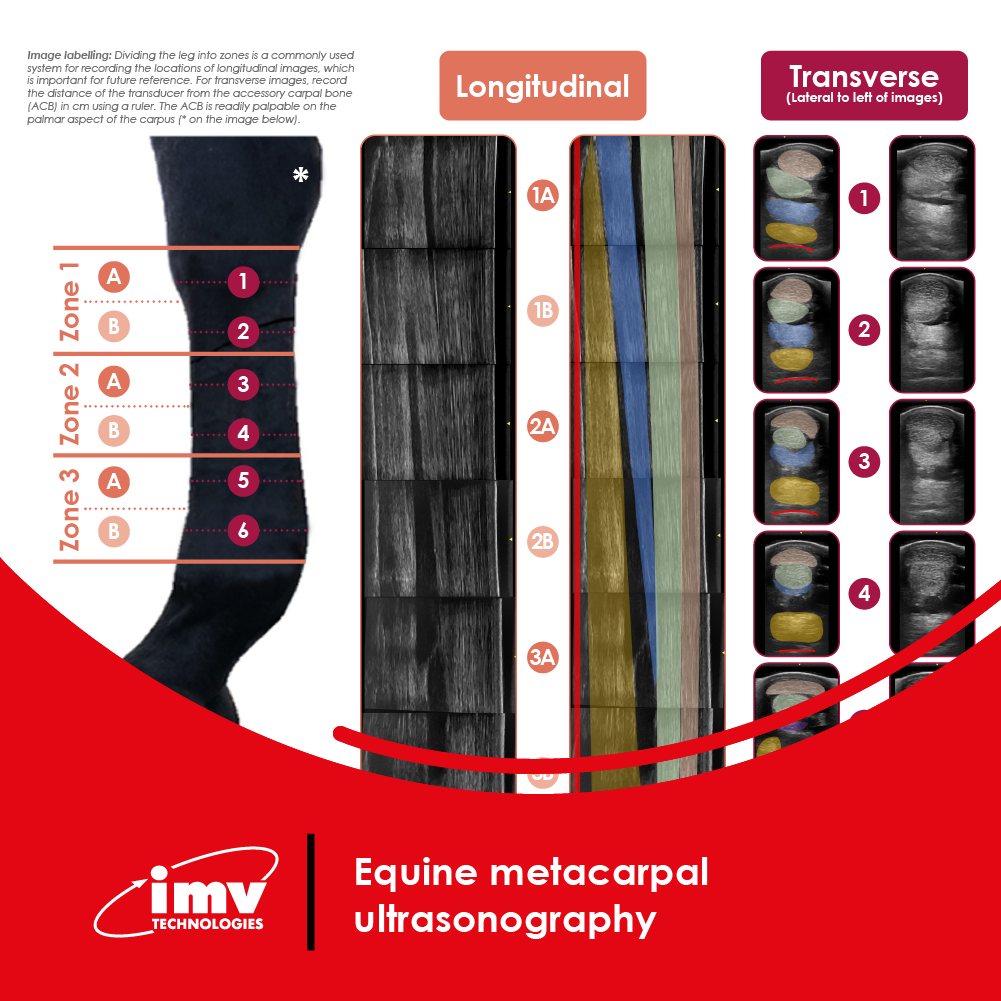
The Academy section is a pivotal knowledge center for the farm animal industry, particularly in artificial insemination and veterinary imaging, providing up-to-date educational resources and training. IMV Technologies Academy offers flexible learning options, including technical articles, blogs, on-demand courses, and replay webinars, enabling clients to access the latest advancements in the industry. Expert-led materials across various species ensure comprehensive knowledge enhancement, helping clients stay competitive and improve their technical skills in their respective specialties. This resource is crucial for staying informed and excelling in animal reproduction practices.
Télécharger le catalogue 2026 de la Field Academy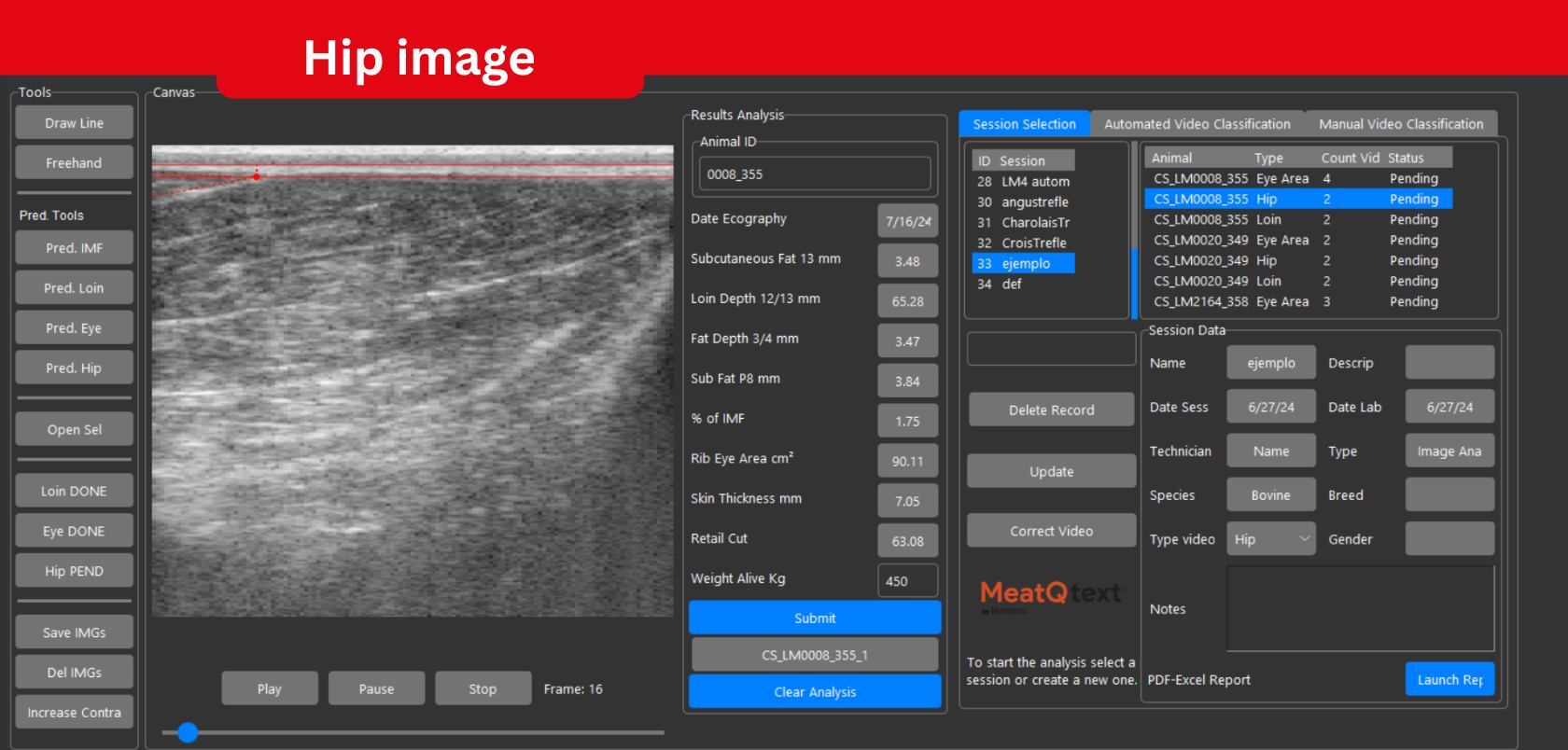




Scope:The objective of the training is to give a deeper understanding of milt...
Scope:The objective of the training is to give a deeper understanding of milt...

2 daysREF 026348

2 daysREF 026346